quickref.rst
With this commit there is now only one entry point into the whole documentation, which describes the general MicroPython language, and then from there there are links to information about specific platforms/ports. This commit doesn't change content (almost, it does fix a few internal links), it just reorganises things.
Quick reference for the WiPy
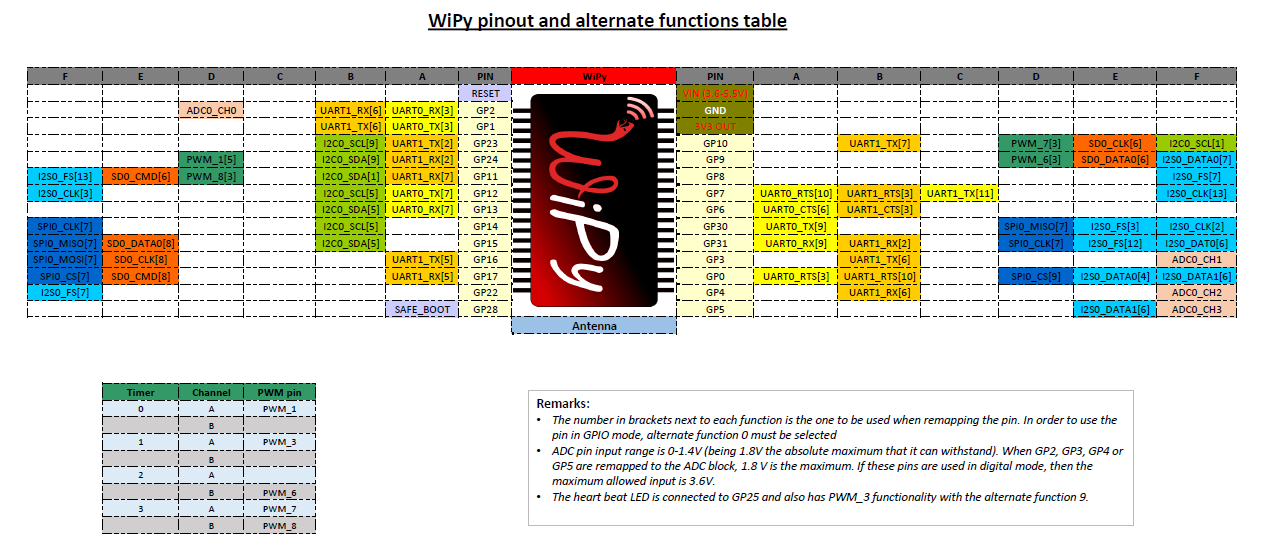
Below is a quick reference for CC3200/WiPy. If it is your first time working with this board please consider reading the following sections first:
General board control (including sleep modes)
See the :mod:`machine` module:
import machine
help(machine) # display all members from the machine module
machine.freq() # get the CPU frequency
machine.unique_id() # return the 6-byte unique id of the board (the WiPy's MAC address)
machine.idle() # average current decreases to (~12mA), any interrupts wake it up
machine.sleep() # everything except for WLAN is powered down (~950uA avg. current)
# wakes from Pin, RTC or WLAN
machine.deepsleep() # deepest sleep mode, MCU starts from reset. Wakes from Pin and RTC.Pins and GPIO
See :ref:`machine.Pin <machine.Pin>`.
from machine import Pin
# initialize GP2 in gpio mode (alt=0) and make it an output
p_out = Pin('GP2', mode=Pin.OUT)
p_out.value(1)
p_out.value(0)
p_out.toggle()
p_out(True)
# make GP1 an input with the pull-up enabled
p_in = Pin('GP1', mode=Pin.IN, pull=Pin.PULL_UP)
p_in() # get value, 0 or 1Timers
See :ref:`machine.TimerWiPy <machine.TimerWiPy>` and :ref:`machine.Pin <machine.Pin>`.
Timer id's take values from 0 to 3.:
from machine import Timer
from machine import Pin
tim = Timer(0, mode=Timer.PERIODIC)
tim_a = tim.channel(Timer.A, freq=1000)
tim_a.freq(5) # 5 Hz
p_out = Pin('GP2', mode=Pin.OUT)
tim_a.irq(trigger=Timer.TIMEOUT, handler=lambda t: p_out.toggle())PWM (pulse width modulation)
See :ref:`machine.Pin <machine.Pin>` and :ref:`machine.Timer <machine.Timer>`.
from machine import Timer
# timer 1 in PWM mode and width must be 16 buts
tim = Timer(1, mode=Timer.PWM, width=16)
# enable channel A @1KHz with a 50.55% duty cycle
tim_a = tim.channel(Timer.A, freq=1000, duty_cycle=5055)ADC (analog to digital conversion)
See :ref:`machine.ADC <machine.ADC>`.
from machine import ADC
adc = ADC()
apin = adc.channel(pin='GP3')
apin() # read value, 0-4095UART (serial bus)
See :ref:`machine.UART <machine.UART>`.
from machine import UART
uart = UART(0, baudrate=9600)
uart.write('hello')
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytesSPI bus
See :ref:`machine.SPI <machine.SPI>`.
from machine import SPI
# configure the SPI master @ 2MHz
spi = SPI(0, SPI.MASTER, baudrate=200000, polarity=0, phase=0)
spi.write('hello')
spi.read(5) # receive 5 bytes on the bus
rbuf = bytearray(5)
spi.write_readinto('hello', rbuf) # send and receive 5 bytesI2C bus
See :ref:`machine.I2C <machine.I2C>`.
from machine import I2C
# configure the I2C bus
i2c = I2C(baudrate=100000)
i2c.scan() # returns list of slave addresses
i2c.writeto(0x42, 'hello') # send 5 bytes to slave with address 0x42
i2c.readfrom(0x42, 5) # receive 5 bytes from slave
i2c.readfrom_mem(0x42, 0x10, 2) # read 2 bytes from slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10
i2c.writeto_mem(0x42, 0x10, 'xy') # write 2 bytes to slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10Watchdog timer (WDT)
See :ref:`machine.WDT <machine.WDT>`.
from machine import WDT
# enable the WDT with a timeout of 5s (1s is the minimum)
wdt = WDT(timeout=5000)
wdt.feed()Real time clock (RTC)
See :ref:`machine.RTC <machine.RTC>`
from machine import RTC
rtc = RTC() # init with default time and date
rtc = RTC(datetime=(2015, 8, 29, 9, 0, 0, 0, None)) # init with a specific time and date
print(rtc.now())
def alarm_handler (rtc_o):
pass
# do some non blocking operations
# warning printing on an irq via telnet is not
# possible, only via UART
# create a RTC alarm that expires after 5 seconds
rtc.alarm(time=5000, repeat=False)
# enable RTC interrupts
rtc_i = rtc.irq(trigger=RTC.ALARM0, handler=alarm_handler, wake=machine.SLEEP)
# go into suspended mode waiting for the RTC alarm to expire and wake us up
machine.sleep()SD card
See :ref:`machine.SD <machine.SD>`.
from machine import SD
import os
# clock pin, cmd pin, data0 pin
sd = SD(pins=('GP10', 'GP11', 'GP15'))
# or use default ones for the expansion board
sd = SD()
os.mount(sd, '/sd')WLAN (WiFi)
See :ref:`network.WLAN <network.WLAN>` and :mod:`machine`.
import machine
from network import WLAN
# configure the WLAN subsystem in station mode (the default is AP)
wlan = WLAN(mode=WLAN.STA)
# go for fixed IP settings
wlan.ifconfig(config=('192.168.0.107', '255.255.255.0', '192.168.0.1', '8.8.8.8'))
wlan.scan() # scan for available networks
wlan.connect(ssid='mynetwork', auth=(WLAN.WPA2, 'mynetworkkey'))
while not wlan.isconnected():
pass
print(wlan.ifconfig())
# enable wake on WLAN
wlan.irq(trigger=WLAN.ANY_EVENT, wake=machine.SLEEP)
# go to sleep
machine.sleep()
# now, connect to the FTP or the Telnet server and the WiPy will wake-upTelnet and FTP server
See :ref:`network.Server <network.Server>`
from network import Server
# init with new user, password and seconds timeout
server = Server(login=('user', 'password'), timeout=60)
server.timeout(300) # change the timeout
server.timeout() # get the timeout
server.isrunning() # check whether the server is running or notHeart beat LED
See :mod:`wipy`.
import wipy
wipy.heartbeat(False) # disable the heartbeat LED
wipy.heartbeat(True) # enable the heartbeat LED
wipy.heartbeat() # get the heartbeat state